Welcome to Daily Banking Digest, your premier source for the latest news and insights on March 09, 2024, focusing on banking, the economy, and finance. Our platform offers a comprehensive overview of the day’s most critical financial stories, market trends, and economic developments. Whether you’re a professional in the financial sector, an investor monitoring market movement, or someone interested in staying informed about the economic landscape, Daily Banking Digest provides reliable, up-to-date information.
Join our Telegram Channel for Daily PDF in your Inbox – Click Here
Table of Contents
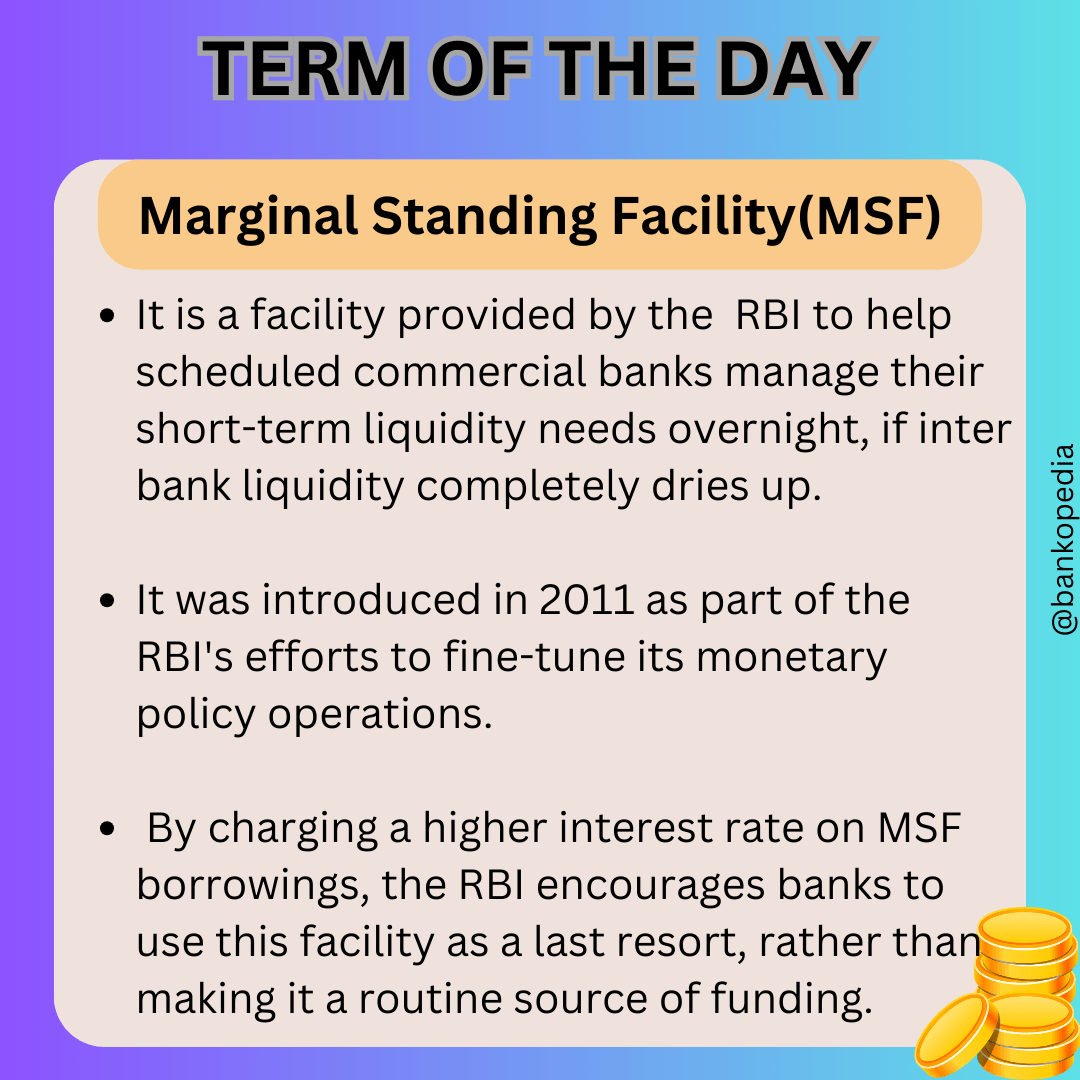
Indian Banks’ Association agree on 17% wage hike, saturdays off for employees.
The Indian Banks’ Association (IBA) and bank employee unions have agreed on a 17% annual wage hike for 8 lakh public sector bank employees, effective from November 2022. The agreement also includes recognition of all Saturdays as holidays, pending government notification.

Key Points:
Wage Hike: – 17% annual wage hike for 8 lakh bank employees – Effective from November 2022 – Additional yearly outgo of Rs 8,284 crore for public sector banks
Working Hours: – All Saturdays recognized as holidays, pending government notification
Leave Benefits: – Women employees allowed one day sick leave per month without medical certificate – Accumulated privilege leave can be encashed up to 255 days at retirement or death
Pension Benefits: – Monthly ex-gratia amount for retired employees who became eligible for pension on or before October 31, 2022
NCLT turns down IFFCO plea for relief in case against Triumph Offshore, Swan Energy
The National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) has rejected IFFCO’s request for relief against its joint venture Triumph Offshore and partner Swan Energy. IFFCO had alleged mismanagement and oppression, but the court found that IFFCO’s director was also on Triumph Offshore’s board. The court has directed Triumph Offshore to hold a board meeting and discuss the issues raised by IFFCO.

Key Points
IFFCO’s Petition – IFFCO alleged mismanagement and oppression by Triumph Offshore. – Claimed that Triumph Offshore was issuing securities to Swan Energy to pre-pay debt, diluting IFFCO’s stake. – Stated that Triumph Offshore had arranged a loan of over ₹1,600 crore and had not taken steps to charter a floating storage gasification unit (FRSU).
Responses from Swan Energy and Triumph Offshore – Denied allegations of mismanagement and oppression. – Stated that all decisions were taken with the knowledge of IFFCO’s directors. – Explained the delay in securing a charter for the FRSU and the decision to raise funds through an inter-corporate loan and a rights issue. – Accused IFFCO of being a passive investor with no direct financial obligations to lenders.
NCLT’s Decision – Rejected IFFCO’s request for relief due to its director’s presence on Triumph Offshore’s board. – Directed Triumph Offshore to hold a board meeting and discuss the issues raised by IFFCO. – Scheduled the next hearing for April 4.
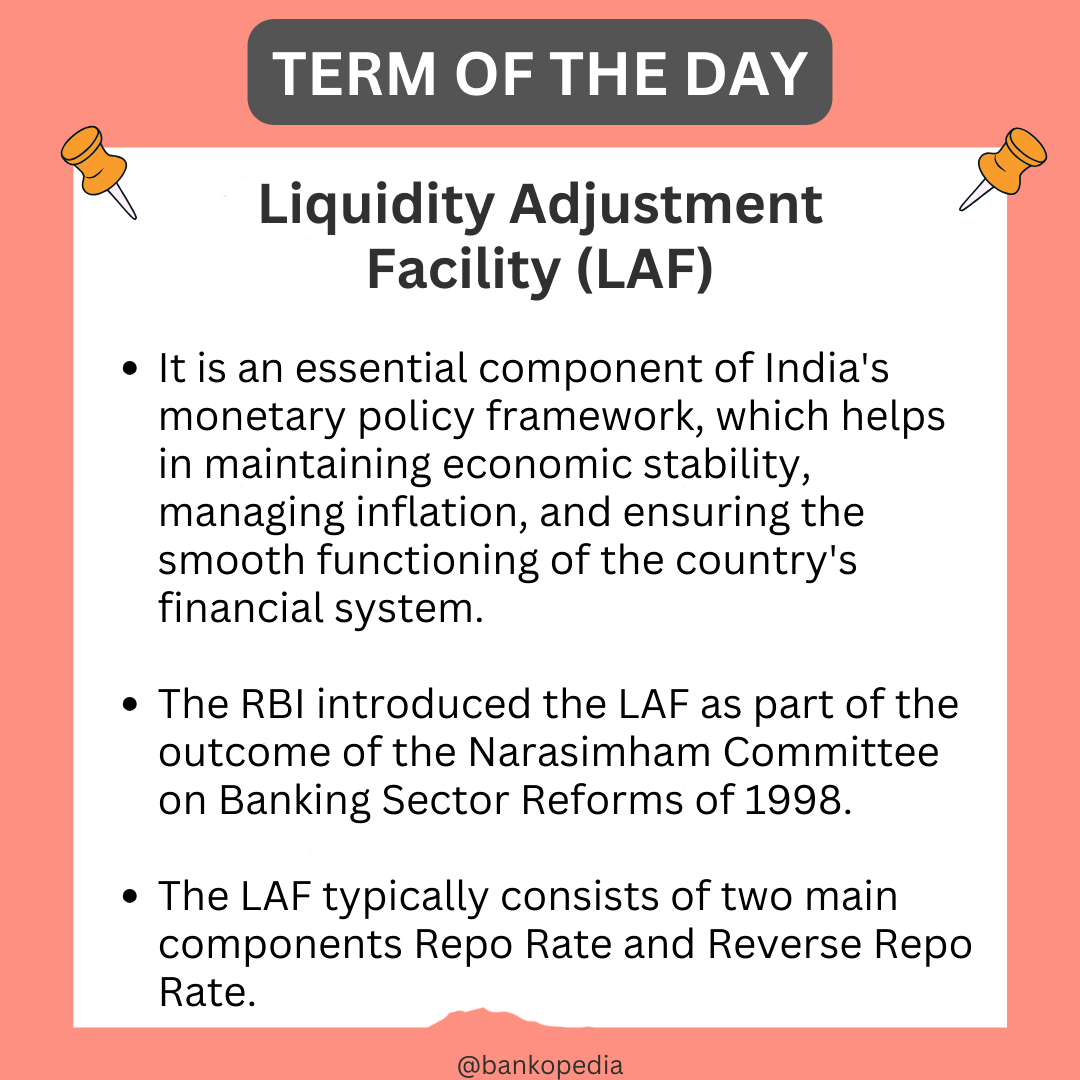
Interest rates on small saving schemes to remain unchanged in April-June quarter.
The Finance Ministry has announced that interest rates on small savings schemes, including PPF and Sukanya Samridhi, will remain unchanged for the April-June quarter. The PPF interest rate will remain at 7.1%, while the Sukanya Samridhi scheme will continue to offer an interest rate of 8.2%.
Key Points:
Interest Rate Unchanged: – No change in interest rates for small savings schemes for the April-June quarter.
PPF Interest Rate: – PPF interest rate remains at 7.1%.
Sukanya Samridhi Interest Rate: – Sukanya Samridhi scheme interest rate remains at 8.2%.
Small Savings Schemes Basket: – Small savings schemes basket includes 12 instruments, including PPF, NSC, KVP, and Sukanya Samridhi Scheme.
Interest Rate Resetting: – Interest rates are reset at the beginning of each quarter. – Theoretically, interest rates are based on government security yields, but other factors are also considered in practice.
IT Dept expands list of payments received by IFSC units for TDS relaxation.
The Income Tax Department has exempted 14 types of units established in the International Financial Services Centre (IFSC) from Tax Deducted at Sources (TDS) to promote business expansion and investments. The exemption applies to receipts such as professional fees, commissions, and interest income, subject to certain conditions.

Key Points:
Exempted Units:
- Banks
- Insurance intermediaries
- Finance companies
- Broker dealers
- Investment advisors
- Custodians
- Trade finance services
- Fintech companies
Exempted Receipts:
- Professional fees
- Commissions
- Dividend income
- Interest income on external commercial borrowing
- Referral fees
- Brokerage income
- Investment advisory fees
- Credit rating fees
- Trusteeship fees
- Technical fees
Conditions for Exemption:
- Payee must furnish a statement-cum-declaration (Form No. 1) providing details of previous years for which Section 80LA deduction is claimed.
- Payer must not deduct tax after receiving Form No. 1 from the payee.
- Payer must furnish particulars of payments made without TDS deduction in TDS statement.
Benefits of Exemption:
- Mitigates cash trap for IFSC units.
- Enhances the appeal of IFSC as a global investment destination.
- Accelerates FDI flows in emerging financial/economic zones.
- Provides an incentive for companies to establish operations in IFSC.
India, EFTA bloc likely to sign free trade pact on March 10
India and the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) countries are set to sign a bilateral free trade agreement on March 10th. The agreement aims to boost trade, investment, job creation, and economic growth. It is expected to attract $100 billion in investments from EFTA countries over 15 years, creating an estimated one million jobs in India. The agreement will also reduce India’s trade deficit with EFTA countries.
Key Points:
Investment and Employment: – EFTA countries have committed to investing $100 billion in India over 15 years, generating one million jobs. – Investments will focus on areas such as pharmaceuticals, medical devices, chemicals, food processing, and engineering products.
Trade Deficit Reduction: – The agreement is expected to reduce India’s trade deficit with EFTA countries, which currently stands at $18.58 billion.
Negotiation Timeline: – Negotiations for the free trade agreement began in October 2016.
Agreement Contents: – The agreement includes chapters on trade in goods, rules of origin, trade in services, investment promotion, trade and sustainable development, and customs and trade facilitation.
Impact on Other FTA Negotiations: – The signing of the India-EFTA agreement is expected to boost India’s ongoing FTA negotiations with other partners, such as the EU and the UK.
Maritime trade navigating troubled waters: UNCTAD
The Suez and Panama canals, two major global maritime trade waterways, have experienced a significant decline in ship transits due to disruptions in the Red Sea, Black Sea, and Panama Canal. This has resulted in increased shipping costs, longer routes, and environmental concerns.
Key Points
Disruptions in Major Trade Waterways – Ship transits through the Suez Canal have decreased by 40% compared to peak levels. – The number of ships passing through the Panama Canal has dropped by 40% since January 2021.
Causes of Disruptions – Escalating attacks on ships in the Red Sea. – War in Ukraine affecting the Black Sea. – Climate-induced droughts in the Panama Canal.
Impact on Global Trade – Disruptions have far-reaching implications for inflation, food security, and energy security. – 22% of global seaborne container trade passed through the Suez Canal in 2023.
Re-routing of Ships – Ships are avoiding the Red Sea due to security risks, opting for a longer route around Africa. – More oil tankers are re-routing through the Cape of Good Hope. – The number of car-carrying ships using the Red Sea has dropped significantly.
Environmental Impact – Re-routed vessels are increasing speeds to cover longer distances, eroding environmental gains from “slow steaming.” – Rerouting from the Suez Canal to the Cape of Good Hope increases greenhouse gas emissions by 70%.
Economic Impact – Container freight rates on Asia-Pacific to Europe routes have risen sharply. – Freight rate increases have extended to distant locations, such as Asia to the US West Coast.
Rail Vikas Nigam Limited bags multiple contracts
Rail Vikas Nigam Ltd (RVNL) has secured multiple orders for the development and augmentation of electrical infrastructure in Himachal Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh. These orders include the supply, installation, and commissioning of 11 KV lines and distribution infrastructure, with a combined value of over ₹1.5 billion.
Key Points:
Order from Madhya Pradesh PoorvKshetra Vidyut Vitaran Company Ltd, Jabalpur:
- Supply, installation, testing, and commissioning of 11 KV line associated works in Jabalpur city
- Contract period: 24 months
- Value: Over ₹251 crore
Orders from Himachal Pradesh State Electricity Board Ltd:
- Development of distribution infrastructure in the South zone of Himachal Pradesh
- Value: Approximately ₹888 crore
- Development of distribution infrastructure in the North zone of Himachal Pradesh
- Value: Approximately ₹410 crore
ICAI to hold foundation and intermediate exams thrice a year
The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) has announced that it will now hold its Foundation and Intermediate Course exams thrice a year, in January, May/June, and September, instead of twice a year in May and November. This decision aims to provide students with more opportunities to appear for the exams and reduce the waiting period between exams.
Key Points:
Exam Frequency: – Exams will now be held thrice a year: January, May/June, and September. – Interval between exams reduced from 6 months to 4 months.
Benefits for Students: – Students can appear for exams without waiting for 2 months. – More opportunities to sit for the exam.
Exam Calendar for Final Course: – Remains unchanged, held in May and November each year.
ICAI Membership and Students: – ICAI has 4 lakh members and 8.5 lakh students. – Aim to have 30 lakh chartered accountants by 2047.
Tech-Savvy Professionals: – ICAI has redesigned its education and training scheme to produce skilled and technology-savvy accounting professionals. – New curriculum implemented on July 1, 2023, focuses on technology proficiency.
ESAF Small Finance Bank to raise ₹135 crore via issuance of tier-II bonds.
ESAF Small Finance Bank plans to raise up to ₹135 crores through the issuance of Basel-II compliant tier-II bonds. The bank has witnessed significant growth in deposits and advances, with net profit tripling in the third quarter of 2023.
Key Points:
Fund Raising: – ESAF Small Finance Bank to raise up to ₹135 crores through tier-II bonds. – Bonds will be listed, rated, taxable, unsecured, transferable, redeemable, and fully paid-up.
Financial Performance: – Deposits increased by 40.6% to ₹18,860 crore in Q3 2023. – Advances under management rose by 35.9% to ₹18,149 crore. – Net profit tripled to ₹112.1 crore in Q3 2023.
Network Expansion: – Bank has 731 banking outlets and 600 ATMs across 21 states and 2 union territories.
NPCI ties up with Nepal’s Fonepay for cross-border merchant payments.
NPCI International Payments (NIPL) has partnered with Nepal’s Fonepay Payment Service to enable cross-border UPI transactions between India and Nepal. This agreement will facilitate QR-code-based, person-to-merchant (P2M) UPI payments, initially allowing Indian consumers to make payments at businesses in Nepal. The partnership aims to enhance economic ties, commerce, and tourism between the two nations.
Key Points:
Cross-Border UPI Transactions: – NIPL and Fonepay have partnered to enable cross-border UPI transactions between India and Nepal. – Indian consumers can now make instant, secure, and convenient UPI payments at businesses in Nepal.
Economic Benefits: – The cross-border payment solution is expected to improve economic ties, commerce, and tourism between India and Nepal. – It will promote economic prosperity and progress in both countries.
Fonepay Payment Service: – Fonepay is a Payment System Operator (PSO) and a subsidiary of the F1Soft Group. – It facilitates inter-bank person-to-person (P2P) and person-to-merchant (P2M) transactions through its interoperable network and mobile platforms. – Fonepay is regulated by Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB) and is Nepal’s first mobile payment network to be licensed as a PSO.
Previous Agreement: – NPCI International recently signed an MoU with Greece-based Eurobank S.A. to streamline cross-border payments between Greece and India using UPI rails. – This agreement enables Foreign Inward Remittance transactions from Greece to India.
LPG cylinder prices cut by Rs 100 to ease Indian households’ cost burden: PM Modi
India has reduced LPG cylinder prices by Rs. 100 per cylinder, providing relief to households amidst rising inflation and upcoming elections. The move aims to ease financial burdens, promote healthier cooking practices, and empower women.
Key Points:
LPG Cylinder Price Cut:
- LPG cylinder prices reduced by Rs. 100 per cylinder.
- Price of a cylinder in Delhi reduced to Rs. 803.
- Prices in Mumbai, Kolkata, and Chennai also reduced.
PM Modi’s Statement:
- Prime Minister Modi announced the price cut on Women’s Day, highlighting its benefits for women.
- The move aligns with the government’s commitment to empowering women and improving their quality of life.
Additional Measures:
- Government continues to provide a subsidy of Rs. 300 per LPG cylinder to economically weaker women under the Ujjwala Yojana.
- Cooking gas prices were previously reduced by Rs. 200 per cylinder in August 2023.
Political Context:
- The price cut comes ahead of the Lok Sabha elections.
- The government aims to address inflationary pressures and ease financial burdens on households.
- The opposition has criticized the government’s handling of rising prices.
DA hiked to 50%, HRA, other components to rise: How much will salary increase for central government employees, pensioners?
The central government has increased the dearness allowance (DA) and dearness relief (DR) for its employees and pensioners by 4%, bringing it to 50%. This hike will benefit approximately 49.18 lakh employees and 67.95 lakh pensioners. The increased DA will also lead to a rise in other allowances and components of the salary, such as house rent allowance (HRA), daily allowance, and gratuity ceiling.
Key Points:
DA and DR Hike: – DA for central government employees increased by 4% to 50%. – DR for central government pensioners increased by 4% to 50%. – Effective from January 1, 2024.
Impact on Salary: – Salary of central government employees will increase due to higher DA. – HRA, daily allowance, and other components will also increase as DA reaches 50%.
Impact on Pension: – Monthly pension of central government pensioners will increase due to higher DR.
Allowances Linked to DA: – House rent allowance (HRA) – Children’s education allowance – Special allowance for childcare – Hostel subsidy – TA on transfer (transportation of personal effects) – Gratuity ceiling – Dress allowance – Mileage allowance for own transport – Daily allowance
HRA Revision: – HRA rates revised to 30%, 20%, and 10% of basic pay in X, Y, and Z cities, respectively, when DA reaches 50%.
Other Components: – Special allowance for child care, gratuity ceiling, dress allowance, and daily allowance will be increased by 25% when DA reaches 50%.
Govt extends export benefits under RoDTEP scheme to SEZ units
The Indian government has extended the Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP) scheme to companies in special economic zones (SEZs) and export-oriented units (EOUs). This move aims to support exporters amidst global economic uncertainties and supply chain disruptions. The scheme provides refunds for various taxes and duties incurred during the production and distribution of exported goods.
Key Points:
Extension of RoDTEP Benefits: – RoDTEP benefits extended to companies in SEZs and EOUs. – These sectors contribute approximately 25% of India’s total exports.
Scheme Details: – RoDTEP refunds various central and state duties, taxes, and levies imposed on input products. – Current RoDTEP rates range from 0.3% to 4.3%. – The scheme has provided support amounting to Rs 42,000 crore to over 10,500 export items since its inception in January 2021.
Budget and Duration: – The scheme has a budget of Rs 15,070 crore for the current financial year. – An additional 10% increase in the budget is expected in 2024-25. – The extension of the scheme to additional sectors is currently valid until September 30, 2024.
Benefits for Exporters: – Enhanced export competitiveness in international markets. – Support for key sectors such as engineering, textiles, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
Goal of RoDTEP: – To refund taxes and duties that are not rebated under any other scheme. – To cover various central, state, and local duties/taxes/levies incurred in the production and distribution of exported products.
EPFO gives relief to these EPF members from submitting joint declaration form.
The Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO) has issued a circular providing relief to certain EPF account holders from submitting a joint declaration form for contributing to their EPF account on a basic salary higher than the statutory wage ceiling of Rs 15,000 per month. However, this relief does not apply to those who have applied for the higher pension under the Employees’ Pension Scheme (EPS).
Key Points:
Relief from Joint Declaration Form:
- Applies to EPF members who left employment or died before October 31, 2023.
- Applies to existing EPF members who are already contributing on pay exceeding the statutory limit and their employers are paying administrative charges.
New Joint Declaration Format:
- Must be submitted when joining the EPF scheme with a basic salary exceeding the statutory limit.
- Must be submitted when switching jobs with a basic salary exceeding the statutory limit.
EPF Scheme Rules:
- Employees with a monthly basic salary not exceeding Rs 15,000 are automatically eligible to join the EPF scheme.
- Employees with a monthly basic salary exceeding Rs 15,000 must submit a joint declaration form to contribute on a higher basic pay.
- Employees who join the EPS must have a monthly basic salary not exceeding the statutory wage limit.
Employer and Employee Contributions:
- Both employer and employee contribute 12% of their basic salary to the EPF account.
- 8.33% of the employer’s contribution goes into the EPS, with a maximum contribution of Rs 1,250.
- The balance of the employer’s contribution (3.67%) goes into the provident fund account.
Government exempts certain exporting units from quality control orders with conditions.
The Indian government has exempted advance authorization holders and export-oriented units (EOUs) from mandatory quality control orders (QCOs) for imported goods used as inputs for exports. This exemption is subject to pre-import conditions and the inputs must be utilized in manufacturing export products.
Key Points:
Exemption for Advance Authorization Holders and EOUs: – Advance authorization holders and EOUs are exempted from mandatory QCOs for imported inputs used in export production.
Pre-Import Conditions: – The exemption is subject to pre-import conditions, ensuring that the inputs are used for export manufacturing.
Utilization of Inputs: – The imported inputs must be utilized in the manufacturing of export products.
Disposal of Unutilized Material: – Any unutilized material must be destroyed in the presence of jurisdictional GST/customs authorities.
Purpose of QCOs: – QCOs aim to prevent the import of sub-standard products, curb unfair trade practices, and ensure consumer safety and environmental protection.
Applicability of QCOs: – QCOs apply to both domestically manufactured and imported products.
Government’s Focus: – The government aims to expand the scope of QCOs to enhance the quality ecosystem in India and provide consumers with quality products.
Centre raises M&A thresholds for antitrust regulator’s nod
The Ministry of Corporate Affairs has increased the asset and turnover thresholds for mergers and acquisitions that require approval from the antitrust regulator, reducing the compliance burden for small deals. The new thresholds for domestic and foreign companies have been raised to ₹2,500 crore and $1.25 billion, respectively, for assets, and ₹7,500 crore and $3.75 billion for turnover. The revised thresholds aim to promote ease of doing business and facilitate smoother M&A processes.
Key Points
- Increased Thresholds: The asset and turnover thresholds for M&A deals requiring CCI approval have been raised to ₹2,500 crore and ₹7,500 crore for domestic companies and $1.25 billion and $3.75 billion for foreign companies.
- Domestic Groups: Two domestic groups pursuing M&A will need CCI approval if their combined assets and turnover exceed ₹10,000 crore and ₹30,000 crore, respectively.
- Foreign Groups with India Operations: The thresholds for combined assets and turnover for two foreign groups with India operations have been raised to $5 billion and $15 billion, respectively.
- Exemption for Small Deals: Acquisitions with targets having assets less than ₹450 crore or turnover under ₹1,250 crore are exempt from CCI approval, providing relief for two years.
- Business-Friendly Revisions: The revisions are seen as a positive step towards a more business-friendly environment in India, facilitating smoother M&A processes and reducing regulatory hurdles.
CCI rejects plea to delink penalty from global turnover.
The Competition Commission of India (CCI) has rejected stakeholders’ requests to base antitrust penalties on relevant turnover or profit, as per the Supreme Court’s Excel Crop judgment. Instead, the CCI has implemented a new framework that links the maximum penalty to a firm’s global turnover, potentially increasing penalties for multinational companies and Big Tech.
Key Points:
Stakeholders’ Plea:
- Stakeholders requested penalties to be based on relevant turnover or profit, as per the Excel Crop judgment.
CCI’s Decision:
- CCI rejected the plea, opting for a framework that links the maximum penalty to global turnover.
New Penalty Framework:
- Maximum penalty is up to 10% of the relevant firm’s average global turnover or income for the three preceding financial years.
- In case of cartelisation, the penalty is three times the profit or 10% of the global turnover or income for each year of the agreement, whichever is higher.
Stakeholders’ Other Requests:
- Exclusion of intra-group sales, “other income,” and export turnover from penalty calculations.
CCI’s Response:
- Excluded intra-group sales and other income from calculations.
- Did not exclude export turnover.
Impact:
- The new framework is expected to increase the CCI’s ability to curb antitrust activities involving multinational firms and Big Tech.
Government notifies changes in competition law related to M&As
The Indian government has revised the Competition Act’s Section 5, which governs mergers and acquisitions (M&As), to reduce the regulatory burden on the Competition Commission of India (CCI). The changes include increasing financial thresholds and De Minimis exemptions, resulting in fewer M&A deals requiring CCI approval.
Key Points:
- Increased Financial Thresholds: The existing financial thresholds under Section 5 have been increased by 150%.
- Increased De Minimis Exemptions: The De Minimis or Small Target Exemption thresholds have also been increased.
- Ease of Doing Business: The changes aim to reduce the regulatory burden on businesses and promote ease of doing business in India.
- Reduced CCI Burden: The increased thresholds will reduce the number of M&A deals requiring CCI approval, freeing up the CCI’s resources.
FPIs quizzed on ‘loans’ for trading
The Indian tax authorities have requested information from foreign portfolio investors (FPIs) regarding their borrowing activities for stock exchange trading. The purpose of this inquiry is unclear, but it may be related to tracing potential links between overseas portfolio managers and Indian companies.
Key Points:
1. Information Requested from FPIs – Identities of lenders – Source of lenders’ funds – Nature of agreements between lenders and FPIs
2. Possible Reasons for Inquiry – Tracing indirect links between overseas portfolio managers and Indian entities – Examining potential round-tripping of Indian money through FPIs
3. Tax Implications – Interest paid by non-resident lenders to non-resident borrowers can be taxed in India if the debt is used for business in India. – However, this does not apply to FPIs, which only earn capital gains in India.
4. Authority of I-T Department – The I-T department has the authority to investigate the source of funds to trace the money trail. – There is no tax implication unless the fund claims interest outgo on loans as a deduction to reduce capital gains tax.
5. Previous Inquiries – The I-T department has been raising queries since January to determine the “substance” of FPIs in Mauritius and Singapore. – FPIs from these jurisdictions are exempt from tax on capital gains made on shares purchased before April 2017 and on derivatives trading. – Funds without “substance” may be denied these tax exemptions.
PSU banks ordered to test purity of gold loan book.
The Finance Ministry has instructed state-run banks to review their gold loan processes due to concerns about risky lending practices amid rising gold prices. The ministry has asked banks to assess collateral values, analyze collection charges, and check for any irregularities in gold loan accounts since January 2022.
Key Points:
Concerns about Risky Lending: – Surge in gold prices has led to lenders giving top-up loans over existing debt.
Finance Ministry Directive: – Letter sent to PSU bank chiefs on February 27, 2024, requesting a review of gold loan accounts since January 1, 2022.
Specific Concerns: – Non-compliance with gold loan portfolio regulations. – Disbursement of loans without requisite gold collateral. – Anomalies in collection of fees and interest. – Closure of accounts on the same day or within a few days of disbursement.
Audit Requirements: – Banks asked to audit gold loan portfolio, including accounts disbursed and closed in the last two years. – Verification of collateral gold, purity, and value. – Analysis of collection charges and interest applied. – Identification of irregularities in loan accounts closed within 90 days of disbursement.
Possible Reasons for Review: – To verify if branches boosted gold loan book to meet lending targets. – To ensure interest applied on accounts was recovered from borrowers.
Precursor to RBI Directive: – Communication sent before RBI banned IIFL Finance from giving new gold loans due to lapses in lending process.
End of the road for FAME-II scheme for EVs drives up e2W, e3W demand.
The Indian electric vehicle (EV) market is experiencing a surge in demand, particularly in the two- and three-wheeler segments, as the FAME-II subsidy scheme is set to expire on March 31. The government has been gradually reducing subsidies under the scheme, leading to price reductions by manufacturers to clear inventory. While some OEMs anticipate a temporary spike in sales, others believe that the industry will adapt to the subsidy withdrawal and continue to innovate.
Key Points
FAME-II Scheme Ending – The FAME-II scheme, which provides incentives for the sale of electric vehicles, is set to end on March 31.
Subsidy Reduction – The government has been reducing subsidies under the FAME-II scheme, with the subsidy amount per kWh reduced from Rs 15,000 to Rs 10,000 last June.
Increased Demand – Dealers are reporting a surge in bookings, queries, and sales of electric vehicles in March due to the impending end of the subsidy scheme.
Penetration Increase – The Federation of Automobile Dealers Associations (Fada) expects the penetration of electric three-wheelers to reach 60% by March-end, up from 53.3% in February. – The penetration of electric two-wheelers is also expected to increase to 7% from 5.7% in February.
Price Reductions – Manufacturers are offering discounts and price reductions to clear inventory before the end of the subsidy scheme.
Industry Adaptation – Some OEMs believe that the industry will adapt to the subsidy withdrawal and continue to innovate, maintaining the momentum in EV sales.
OEM Perspectives – Some OEMs, such as Wardwizard Innovations and Mobility, believe that their products are not dependent on FAME subsidies. – Others, such as Lohia Auto Industries, have not seen a significant jump in demand despite the subsidy withdrawal.
Economic shocks hit consumption growth in last decade, says Nomura
Nomura’s Asia Economic Monthly report reveals a slowdown in consumption expenditure growth in India over the past decade, attributed to economic shocks like demonetization, GST implementation, and the COVID-19 pandemic. The report analyzes data from the Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) and highlights key trends in consumption patterns.
Key Points:
1. Consumption Growth Slowdown:
- Compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of rural consumption declined from 6.6% in 2010-12 to 3.1% in 2012-23.
- Urban consumption growth fell from 5.2% to 2.6% during the same period.
2. Nominal Growth and Convergence:
- Nominal rural consumption growth outpaced urban growth over the last decade (2012-2023).
- Rural consumption increased by 164%, while urban consumption grew by 146%, indicating convergence in consumption levels.
3. Inequality Reduction:
- Inequality has reduced for both rural and urban households.
- This is primarily due to top spenders reducing consumption rather than bottom spenders increasing consumption.
- Urban India has a comparatively better situation in terms of inequality reduction.
4. Changing Consumer Tastes:
- Consumers are spending less on food and more on non-food and fuel categories, especially in rural India.
- Within food categories, spending on beverages, processed food, and fruits has increased.
- Consumers are also spending more on conveyance, durable goods, intoxicants, toiletries, and entertainment.
- Spending on clothing, footwear, and education has declined.
UK team heads back to London with Round 14 of FTA talks still open.
The UK and India’s ongoing negotiations for a bilateral free trade agreement (FTA) have not yet reached a conclusion, with the UK team returning to London without a finalized deal. Despite progress, outstanding issues remain, and the UK government emphasizes the importance of a comprehensive and ambitious agreement. India, on the other hand, seeks a balanced and equitable deal that prioritizes long-term economic benefits.
Key Points:
- Negotiations Ongoing: The 14th round of FTA negotiations remains open, with progress continuing.
- Deal Not Finalized: The UK team did not secure all necessary agreements to close outstanding issues.
- UK Commitment: The UK government remains committed to securing a comprehensive FTA and bilateral investment treaty (BIT).
- India’s Priorities: India seeks a balanced, fair, and equitable deal that prioritizes long-term economic benefits.
- Protectionist Economy: The UK minister highlights India’s protectionist economy as a factor in the protracted negotiations.
- Commercial Meaningfulness: The UK emphasizes the importance of a commercially meaningful agreement that benefits businesses.
- Tariffs: The UK seeks significant tariff reductions from India on exports such as food, cars, and whisky.