Table of Contents
When it comes to borrowing money, whether it’s for a mortgage, a car loan, or a credit card, lenders need to assess the risk involved in lending to an individual or a business. This is where credit underwriting comes into play. Credit underwriting is the process of evaluating the creditworthiness of a borrower and determining the terms and conditions of the loan.
In this guide, we will take a closer look at credit underwriting, its importance, and how it works.
What is Credit Underwriting?
Credit underwriting is the process of analyzing a borrower’s creditworthiness to determine their ability to repay a loan. It involves assessing various factors such as credit history, income, employment stability, and debt-to-income ratio.
The goal of credit underwriting is to evaluate the risk associated with lending money and to make informed decisions about whether to approve or deny a loan application.
Importance of Credit Underwriting
Credit underwriting plays a crucial role in the lending process for both borrowers and lenders. For borrowers, it helps determine their eligibility for a loan and the terms and conditions they will be offered. For lenders, it helps mitigate the risk of default and ensures that they are lending to individuals or businesses that have the ability to repay the loan.
By carefully evaluating a borrower’s creditworthiness, lenders can make informed decisions about the amount of money to lend, the interest rate to charge, and the repayment terms.
How Does Credit Underwriting Work?
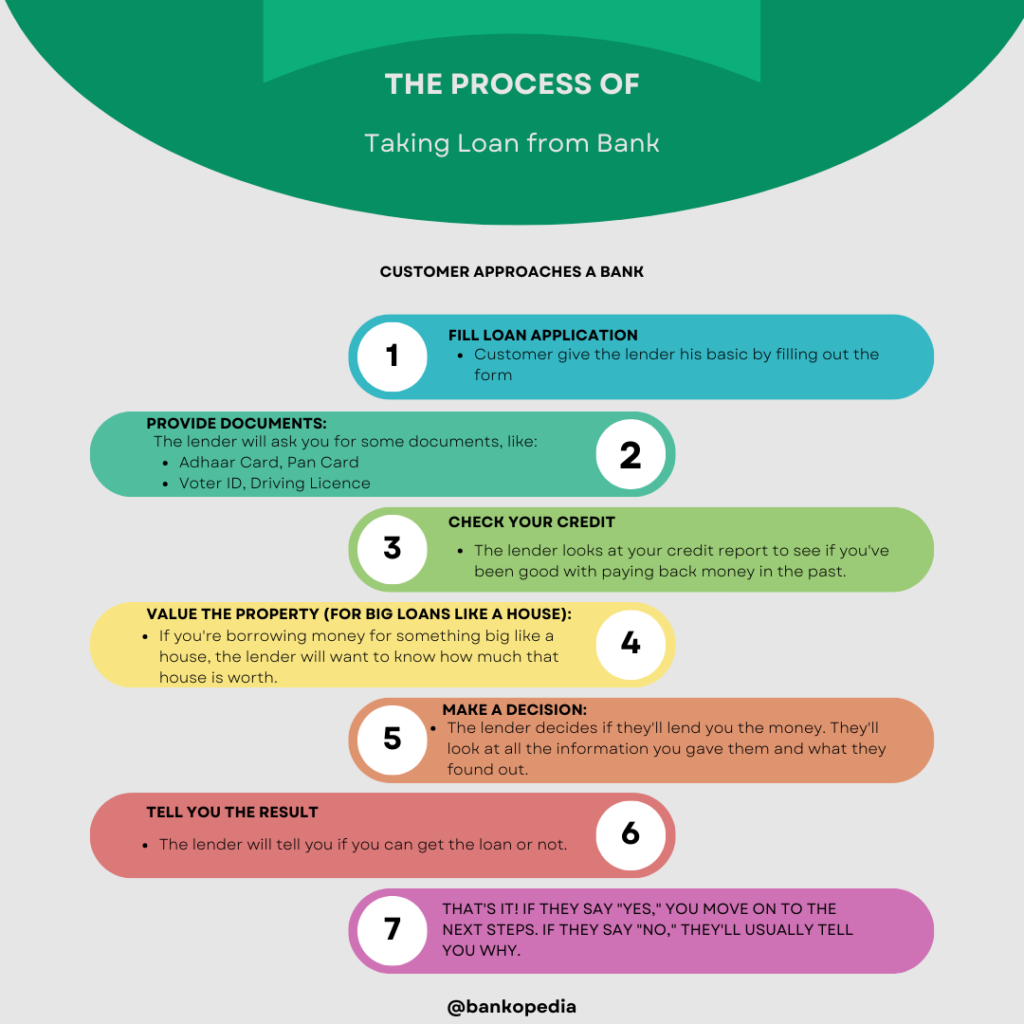
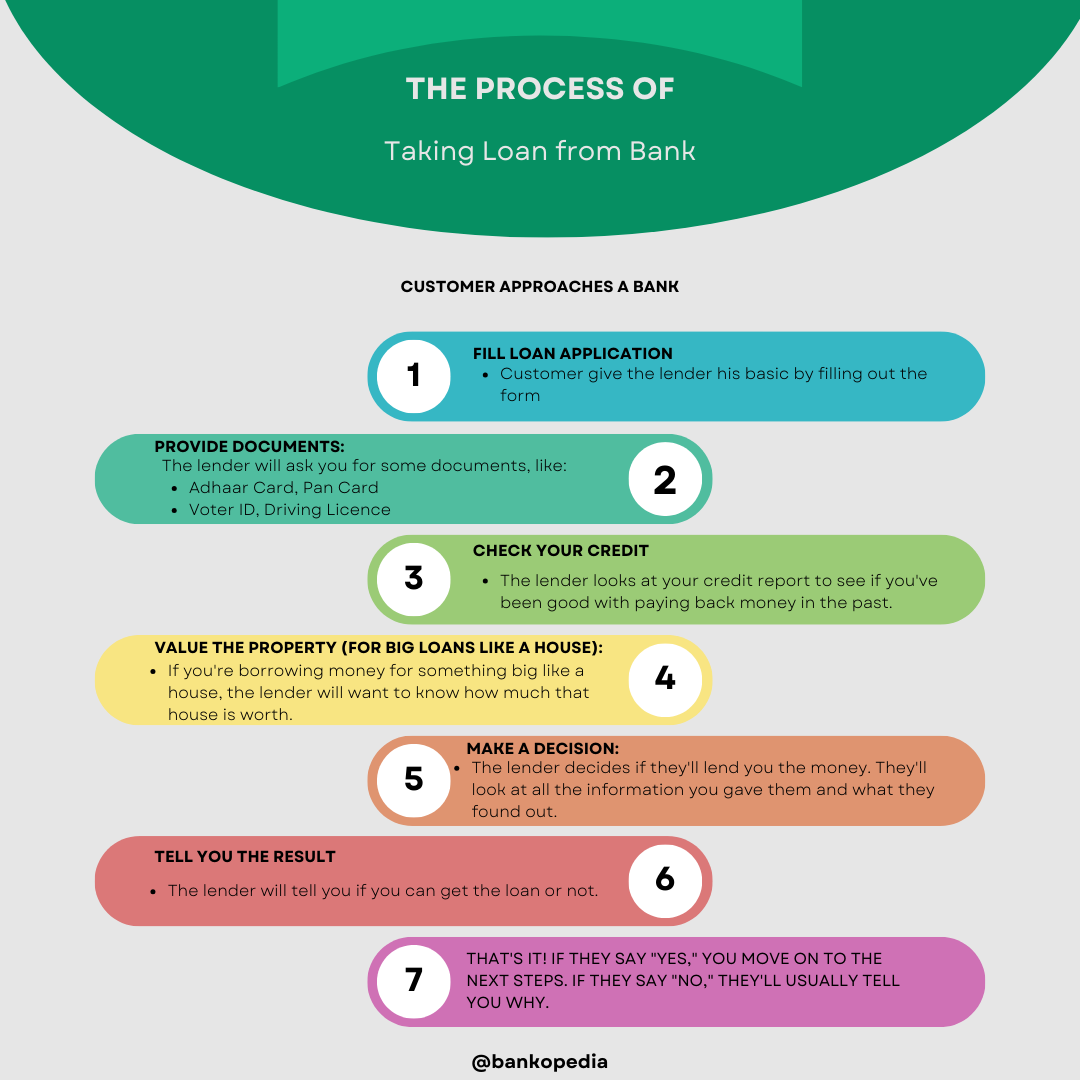
The credit underwriting process typically involves the following steps:
- Application and Documentation: The borrower submits a loan application and provides the necessary documentation, such as proof of income, bank statements, and tax returns.
- Credit Analysis: The lender reviews the borrower’s credit history, including their credit score, payment history, and outstanding debts. They also consider any derogatory marks, such as bankruptcies or foreclosures.
- Income and Employment Verification: The lender verifies the borrower’s income and employment stability to ensure they have a steady source of income to repay the loan.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio: The lender calculates the borrower’s debt-to-income ratio, which compares their monthly debt payments to their monthly income. This helps determine their ability to manage additional debt.
- Collateral Evaluation: In some cases, the lender may require collateral for the loan. They assess the value and condition of the collateral to determine its suitability.
- Decision: Based on the information gathered during the credit underwriting process, the lender makes a decision to approve, deny, or offer alternative loan terms to the borrower.
Conclusion
Credit underwriting is an essential part of the lending process. It helps lenders assess the risk associated with lending money and ensures that borrowers have the ability to repay the loan. By understanding the credit underwriting process, borrowers can take steps to improve their creditworthiness and increase their chances of loan approval.