Welcome to Daily Banking Digest, your premier source for the latest news and insights on February 11, 2024, focusing on banking, the economy, and finance. Our platform offers a comprehensive overview of the day’s most critical financial stories, market trends, and economic developments. Whether you’re a professional in the financial sector, an investor monitoring market movements, or someone interested in staying informed about the economic landscape, Daily Banking Digest provides reliable, up-to-date information.
Download PDF from here
Table of Contents
AI regulation is priority for all but no country will do it, says Spiros Margaris.
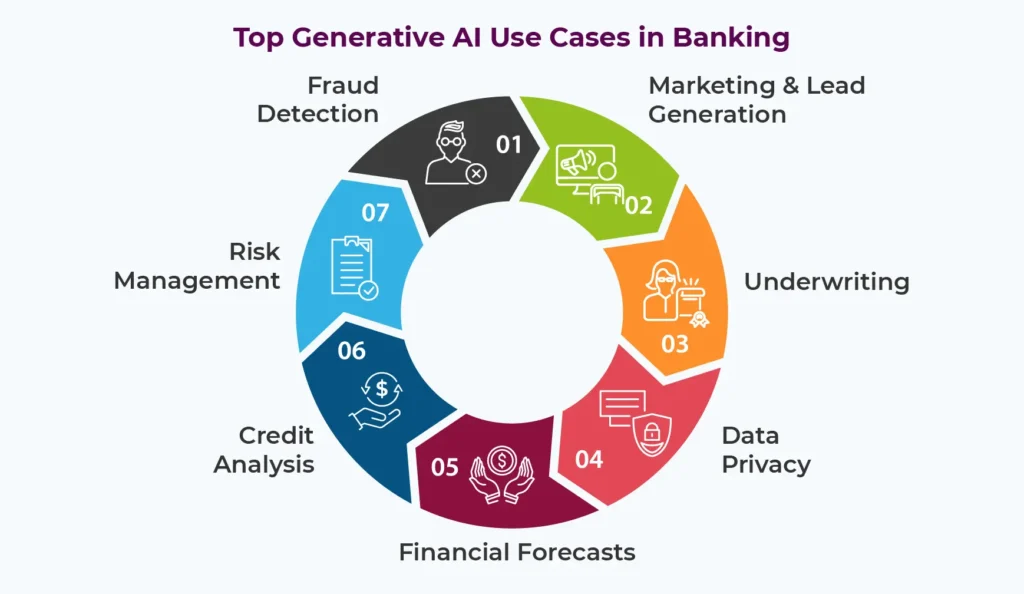
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is expected to significantly affect banking and financial services, and according to Spiros Margaris of Margaris Ventures, India is anticipated to gain substantial economic value from AI by 2025.
Key points:
- AI will transform various aspects of banking, such as KYC processes, loan applications, and risk assessments.
- Spiros Margaris emphasized the need for financial institutions to embrace generative AI and the economic benefits it could bring to India.
- Major financial entities like JP Morgan are investing heavily in AI by hiring experts in the field.
- While there are concerns about AI related to labor, elections, and cybersecurity, Margaris suggests that heavy regulation of AI is unlikely as it could hinder a country’s progress.
- The European Union has passed AI regulations to be effective from 2025, while India plans a more relaxed approach to foster growth and innovation.
- AI’s impact on jobs is debated, with some roles being more susceptible to change than others.
- The use of AI may enhance human skills but could also pose challenges to traditional job roles, with the suggestion that high-paying jobs may be more affected than trade jobs like plumbing or carpentry.
Some Indian companies have already started attributing job losses to AI, citing automation as the reason for workforce reductions.
CBT recommends 8.25% interest on EPF for FY24
The Central Board of Trustees (CBT) of the Employees Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO) has recommended an 8.25% interest rate for the fiscal year 2023-24, which, if approved, will be the highest rate in the last three years.

Key points:
- The proposed interest rate is a 0.10% increase from the previous year’s 8.15%.
- EPFO currently has over six crore (60 million) members.
- Labour Minister Bhupendra Yadav emphasized that the decision aligns with Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s commitment to enhancing social security for Indian workers.
- The recommendation will be sent to the Ministry of Finance for approval. Once ratified, the new interest rate will be credited to subscribers’ accounts.
- The EPFO plans to distribute a total of Rs. 1.07 lakh crores in interest for the year, based on a principal amount of about Rs. 13 lakh crores. This distribution and principal amount have seen an increase of over 17% from the previous fiscal year.
- This performance suggests strong financial health and potentially robust returns for EPFO members.
- The interest rate provided by EPFO has been consistently higher than many other investment options, indicating confidence in EPFO’s investment strategies and their ability to offer attractive returns.
- Historical interest rates show a slight decrease over the past few years, with the rate dropping to a four-decade low of 8.1% in 2021-22 before a marginal increase in 2022-23.
Telangana Govt pegs 2024-25 budget outlay at ₹2.75 lakh crore.

Telangana Government has outlined its budget for the fiscal year 2024-25, with significant allocations toward initiatives promised by the ruling Congress party. Despite financial challenges, there has been an increase in the Gross State Domestic Product, but with mixed performance across various sectors.
Key points-
- The budget for 2024-25 is set at ₹2,75,891 crore, with ₹53,196 crore reserved for six key guarantees promised by the Congress party.
- Deputy Chief Minister and Finance Minister Bhatti Vikramarka Mallu delivered the budget speech, indicating this is an interim budget pending further clarity from the central government’s full budget post-elections.
- The budget details revenue expenditure at ₹2,01,178 crore and capital expenditure at ₹29,669 crore.
- Financial figures from the previous year show a revenue surplus but a fiscal deficit that has grown in the revised estimates for 2023-24.
- Main allocations include substantial funding for Panchayat Raj & Village Development, Irrigation, and Education.
- The Minister criticized past governance for poor financial management and infrastructure spending.
- The GSDP of Telangana has grown, but the economic growth rate has decreased, although it remains higher than the national average.
- There has been a notable decline in agriculture due to adverse seasonal conditions.
- Growth rates in secondary and tertiary sectors have decreased, with significant declines in specific industries like electricity, gas, water supply, and transport services.
- However, the manufacturing sector has seen positive growth, and other sectors like real estate, construction, and mining & quarrying also experienced higher growth rates compared to the previous year.
Government saved over ₹20,000 crore through new accounting mechanisms, says FM Sitharaman
India’s Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced significant savings of over ₹20,000 crore through the implementation of new accounting mechanisms aimed at more efficient fund allocation for government schemes.

Key points:
- The savings have arisen from reforms in the less visible aspects of financial management, including moving the budget announcement date and changing how expenditures are classified.
- The preponement of the Union Budget to February 1 allows states better clarity in their financial planning.
- The shift from classifying expenditures as ‘plan and non-plan’ to ‘capital and revenue’ has increased transparency and reduced discretionary spending.
- The Treasury Single Account (TSA) system and the Single Nodal Account (SNA) system are credited with savings of approximately ₹10,000 crore and ₹10,592 crore respectively.
- The TSA and SNA systems have improved the efficiency of fund use, preventing idle funds in accounts and reducing unnecessary government borrowing.
- The TSA provides a unified view of the government’s cash resources, improving the management of cash resources.
- The SNA system, used for Centrally Sponsored Schemes, ensures timely and stipulated fund allocation to states.
- Sitharaman reflected on the economic growth of India under the Modi government, noting the country’s advancement from the ‘fragile five’ to the 5th largest global economy, with aspirations to become the 3rd largest.
- The White Paper released by the government outlines these reforms and achievements, and the timing was chosen to avoid negatively impacting confidence in India’s economy and institutions.
Soon new series of mobile numbers for commercial, promotional activities by banks, FIs

In an effort to combat online financial frauds, banks and financial institutions will soon transition to sending commercial and promotional messages from a ‘140’ prefix number instead of the current 10-digit mobile numbers.
Key points:
- The decision is part of cybersecurity measures discussed in a meeting led by Financial Services Secretary Vivek Joshi.
- The shift to ‘140xxx’ numbering is mandated by TRAI and is intended to phase out the use of regular 10-digit numbers for commercial activities.
- The meeting also discussed the integration of banks and financial institutions into the Citizen Financial Cyber Fraud Reporting and Management System (CFCFRMS) via API for better fraud detection and management.
- Plans include linking the CFCFRMS platform with the National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (NCRP) to centralize efforts against cybercrime and enable real-time monitoring.
- There’s an emphasis on improving the ‘fraud-to-hold ratio’ by ensuring resources are available around the clock to promptly address complaints.
- Banks and financial institutions are advised to conduct customer awareness programs in regional languages about digital payment security and to standardize information sharing formats for law enforcement agencies.
- The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has developed an AI/ML-based engine named ASTR for detecting mobile connections obtained through fraudulent documents, resulting in the blocking of numerous mobile handsets and SIMs.
- A significant number of entities sending bulk malicious SMS have been blacklisted, and a large number of SMS headers and templates have been disconnected.
- The Pratibimb portal, which plots SIM and IMEI numbers of suspected fraudsters, has led to numerous arrests and the blocking of SIMs and IMEIs, along with the removal of fake links and URLs since its inception in April 2023.
Bank of Maharashtra looks to increase its business in Gujarat by 25%
Bank of Maharashtra (BoM) aims to expand its operations in Gujarat, targeting a 25% growth by the end of the second quarter of FY 2024-25, as announced by Asheesh Pandey, the Executive Director of the bank.

Key points:
- Bank of Maharashtra is doing business worth ₹12,000 crore in Gujarat and aims to increase this to over ₹15,000 crore by the second quarter of the next financial year.
- The growth strategy includes opening more branches in the state, with the 100th branch recently inaugurated in Ahmedabad and the 101st in Vadodara.
- The bank’s board has considered entering Gift City for forex business, though formal application to the regulator is pending.
- Over the past three years, BoM has been on an expansion drive, opening new branches in various Indian states such as Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Jammu, Ludhiana, Rajasthan, and Karnataka.
MCX logs ₹5 crore loss on one-time software fee

Multi Commodity Exchange (MCX), India’s largest commodity exchange, reported a net loss in the December quarter primarily due to expenses related to new software.
Key points:
- MCX experienced a net loss of ₹5 crore in the December quarter, contrasting with a net profit of ₹39 crore in the same period the previous year.
- This loss is attributed to a one-time payment for new software.
- The exchange’s income increased by 27% to ₹209 crore, while expenses almost doubled to ₹223 crore.
- MCX paid ₹146 crore to 63 Moons Technologies for services up to last December and had to continue these services due to a delay in the new software from Tata Consultancy Services (TCS).
- The services of 63 Moons Technologies were extended multiple times, with the final extension costing ₹250 crore for two quarters until December.
- The new software developed by TCS went live in October after receiving necessary approvals.
- MCX reported an EBITDA loss of ₹2 crore for the quarter, compared to a positive EBITDA of ₹44 crore in the corresponding quarter of the previous year, reflecting the payments to the technology vendor and contributions to the Settlement Guarantee Fund (SGF).
- There was a decline of 14% in the average daily turnover in the futures segment, while the options segment more than doubled.
Bankers’ views on RBI Policy
Various banking sector leaders have responded positively to the Monetary Policy Committee’s (MPC) decision to maintain current interest rates, emphasizing the importance of the accompanying regulatory measures for advancing digital infrastructure, customer empowerment, and economic growth.

Key points from various banking leaders:
- Dinesh Khara of SBI approves of the MPC’s decision and the regulatory moves to improve digital robustness and customer empowerment in financial services.
- A K Goel of the Indian Banks’ Association notes the favorable economic conditions and suggests a potential future reduction in rates if inflation consistently hits the target range.
- Zarin Daruwala of Standard Chartered Bank highlights the RBI’s commitment to inflation control and the positive revisions to GDP growth projections, as well as steps to foster the adoption of the Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC).
- Shanti Ekambaram of Kotak Mahindra Bank views the RBI’s policy as a sign of its readiness to manage liquidity and maintain inflation targets and is optimistic about India’s economic growth potential.
- Harsh Dugar of Federal Bank finds the MPC’s announcement expected and sees strong economic activity that will drive credit demand, with new transparency measures for MSME borrowers being particularly beneficial.
- Alok Singh of CSB Bank considers the RBI’s stance on liquidity to be balanced and prudent, suggesting that the RBI may consider easing liquidity or cutting rates post Q2 next year.
- Uttam Tibrewal of AU Small Finance Bank agrees that the RBI’s policies are in line with expectations and anticipates potential monetary easing in the coming quarters as inflation approaches the target range.
RBI wants to drop OTP, but you’ll still need a phone for authentication.

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is urging banks to explore alternatives to SMS-based one-time passwords (OTPs) for second-factor authentication due to the rise in digital frauds and the vulnerabilities associated with OTPs.
Key points:
- While alternatives to OTPs are being considered, they still largely depend on the mobile phone as the central device for authentication.
- Bankers acknowledge the risk of “social engineering” scams, where customers are deceived into revealing passwords or OTPs are intercepted through tactics like SIM swaps.
- Authenticator apps are gaining popularity as a substitute for SMS-based OTPs. These apps generate passwords that users can retrieve on their phones without receiving an SMS.
- Service providers are developing additional methods, such as embedding tokens within mobile applications, although these still depend on the security of the mobile phone.
- Route Mobile reports sending nearly four billion OTPs monthly for various service providers.
- The company’s TruSense division is working on OTP-less authentication methods that involve a direct data connection with the user’s device for secure token exchanges.
- David Vigar, an executive at Route Mobile, notes that while biometrics are not foolproof due to risks like deepfakes, mobile phones remain a reliable identifier in the Indian market due to mandatory identity verification for connections.
- Email is considered less secure for authentication because fake email identities can be easily created without any Know Your Customer (KYC) process.
Indian Overseas Bank to open 88 new branches this year: MD & CEO
Indian Overseas Bank (IOB) has announced plans to open 88 new branches as part of its expansion strategy coinciding with its 88th Foundation Day. The bank also introduced new financial products and services and enhanced its community support initiatives.

Key points:
- IOB plans to open 88 new branches throughout the year to expand its footprint and reinforce its commitment to providing comprehensive financial services.
- On its 88th Foundation Day, IOB launched RuPay Credit Card variants and new savings and current account options, alongside a digital platform for executing online locker agreements.
- The bank has increased interest rates on Rupees Retail Term Deposits for a period of 444 days.
- The revised interest rates are 7.30% for retail term deposits, 7.80% for senior citizens, and 8.05% for Super Senior Citizens.
- As part of their social responsibility, the bank’s Managing Director and CEO Ajay Kumar Srivastava distributed mobility aids to differently abled individuals in association with Ramakrishna Math.
Steel exports up 30 per cent month-on-month, 43 per cent YoY in January.

India’s steel exports have seen significant growth, yet the country continues to be a net importer of steel for the fiscal year from April to January.
Key points:
- India’s steel exports increased by over 30% month-on-month and 43% year-on-year to 0.9 million tonnes in January.
- Despite the increase in exports, India remained a net importer of steel during the first 10 months of the fiscal year, with imports exceeding exports.
- Imports rose 38% year-on-year to 6.8 million tonnes, while exports were at 5.5 million tonnes.
- The rise in global steel prices may limit imports into India for the January-March quarter (Q4 FY24), according to Jayant Acharya, Joint MD and CEO of JSW Steel.
- January saw India becoming a net exporter of steel by a marginal 0.1 million tonnes, breaking a nearly six-month trend of declining exports.
- There’s an expectation of price improvements in the January-March period, which is usually strong for steel mills, with price increases already observed in January and early February.
- The trend in imports for January showed an increase in non-alloyed steel but a decrease in alloyed and stainless steel imports, both year-on-year and month-on-month.
- For the April to January period, non-alloyed steel imports surged while alloyed and stainless steel imports fell.
- Export trends showed a significant year-on-year increase for non-alloyed steel but a decline in the non-alloyed and stainless steel category.
FII to DII ownership ratio at a decade low
Prime Infobase has released a new quarterly shareholding tracker for NSE-listed companies, which highlights significant trends in the investment patterns of different types of investors.

Key points:
- Domestic Mutual Funds (MFs) in India have seen their holdings increase to record levels due to strong net inflows.
- Mutual funds have the largest market cap allocation in the healthcare sector, while Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) have maintained their highest allocation in the Financial Services sector, despite a decrease during the quarter.
- There is a notable reduction in the disparity between FII and Domestic Institutional Investors (DII) holdings, with the FII to DII ownership ratio dropping to the lowest ever at 1.14 in Q3FY24 from a high of 1.99 in Q4FY15, indicating that domestic investment flows are now almost as influential as those from FIIs.
- Private promoter ownership has decreased over recent quarters due to selling off shares, while the government’s shareholding has increased, driven by strong performances from Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs).
NITI Aayog prepares plan for economic transformation of 4 cities, including Mumbai, Varanasi

NITI Aayog is actively developing comprehensive economic plans for several Indian cities to support the broader goal of making India a developed economy by the year 2047.
Key points from the article:
- NITI Aayog’s CEO, BVR Subrahmanyam, announced plans for the economic transformation of Mumbai, Surat, Varanasi, and Vizag.
- There are further plans to extend economic planning to 20-25 additional cities, recognizing their role as hubs of economic activity.
- A vision document for India’s development into a USD 30 trillion economy by 2047 is in the works and is set to be released by Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- The Aayog is shifting its focus from urban planning to economic planning to drive the transformation of these cities.
- Discussions have been held regarding the Mumbai Metropolitan Region (MMR) to boost its GDP to USD 300 billion by 2030.
- The central government has solicited over 10 lakh suggestions from the country’s youth to inform its vision for 2047, which are being processed with artificial intelligence (AI).
- The consolidation of 10 sectoral thematic visions into a single vision for a developed India by 2047 is underway, covering economic, social, environmental, and governance development aspects.











