Table of Contents
Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF), which is used by the RBI to manage liquidity in the banking system. In this article, I will explain the concept of LAF, its components, and how the RBI uses it to drive financial stability.
Introduction to Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF)
Liquidity is the lifeblood of any financial system. It refers to the availability of funds in the system to meet the demand for cash. Banks need liquidity to meet the withdrawal demands of their customers and to lend to other banks or businesses. If there is too much liquidity in the system, it can lead to inflation, while a shortage of liquidity can lead to a credit crunch and a financial crisis.
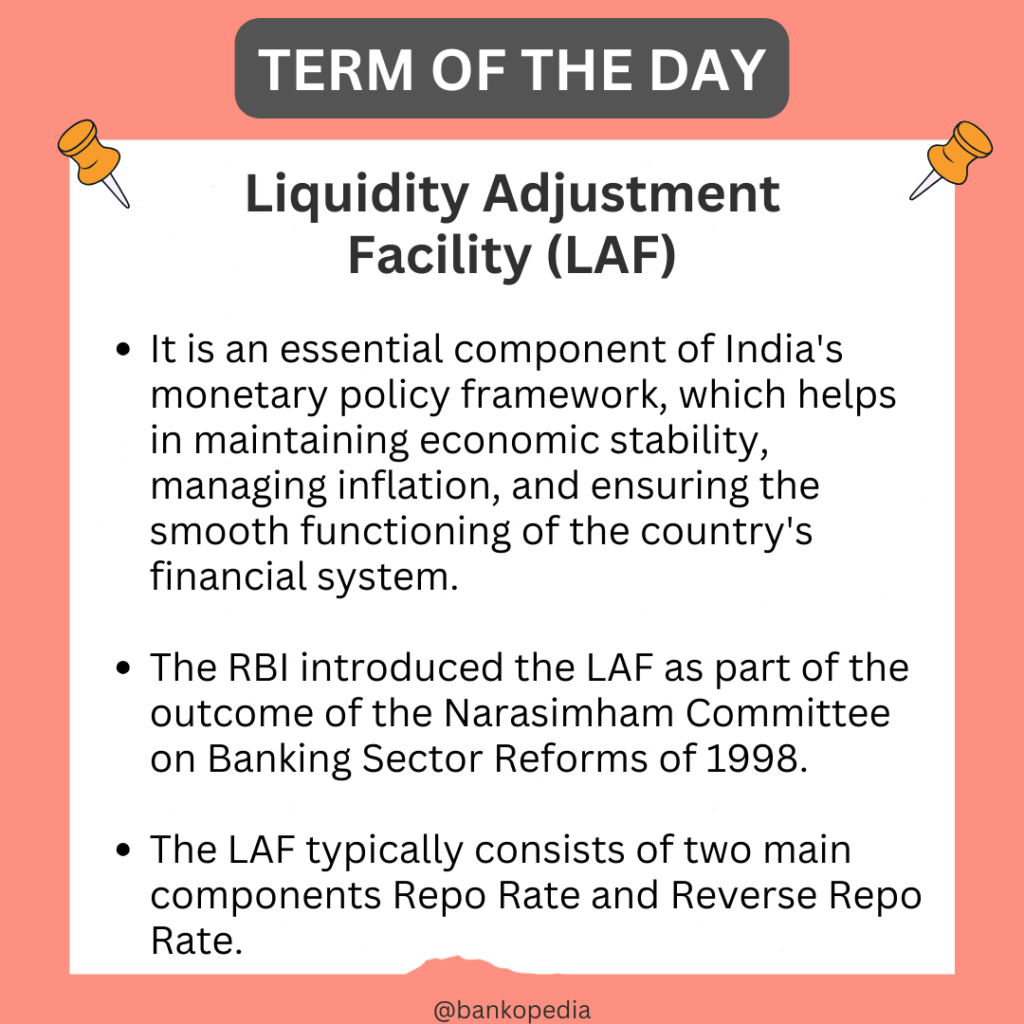
To manage liquidity in the banking system, the RBI has introduced the Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF). LAF is a monetary policy tool that allows banks to borrow money from the RBI on a short-term basis. It consists of two components – Repo and Reverse Repo.
Understanding the role of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the central bank of India, responsible for regulating the monetary and credit system of the country. It was established in 1935 and has its headquarters in Mumbai. The RBI is governed by a central board of directors, which is appointed by the government of India.
The primary objective of the RBI is to maintain price stability and ensure adequate flow of credit to productive sectors of the economy. To achieve this, the RBI uses various monetary policy tools, such as interest rates, reserve ratios, and open market operations. One such tool is the Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF), which allows the RBI to manage liquidity in the banking system.
The concept of monetary policy and its impact on financial stability
Monetary policy refers to the actions taken by a central bank to regulate the supply of money and credit in the economy. The objective of monetary policy is to maintain price stability and support economic growth.
The impact of monetary policy on financial stability is significant. A loose monetary policy, characterized by low-interest rates and easy credit, can lead to asset bubbles and inflation, which can destabilize the financial system. On the other hand, a tight monetary policy, characterized by high-interest rates and tight credit, can lead to a credit crunch and a financial crisis.
Explaining the Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) and its components
The Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) is a monetary policy tool used by the RBI to manage liquidity in the banking system. It consists of two components – Repo and Reverse Repo.
Repo, short for repurchase agreement, is a transaction in which banks borrow money from the RBI by selling government securities. The transaction is reversed after a specified period, during which the banks pay interest on the borrowed amount. The interest rate charged by the RBI on Repo transactions is called the Repo Rate.
Reverse Repo is the opposite of Repo. In a Reverse Repo transaction, banks lend money to the RBI by buying government securities. The interest rate paid by the RBI on Reverse Repo transactions is called the Reverse Repo Rate.
How the RBI uses LAF to manage liquidity in the banking system
The RBI uses the Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) to manage liquidity in the banking system. When there is excess liquidity in the system, the RBI conducts Reverse Repo transactions, which absorbs liquidity from the system. On the other hand, when there is a shortage of liquidity, the RBI conducts Repo transactions, which injects liquidity into the system.
The RBI also uses the LAF to signal its monetary policy stance. For example, if the RBI wants to tighten monetary policy, it can raise the Repo Rate, which makes borrowing more expensive for banks and reduces the supply of credit in the system.
A numerical example to illustrate the functioning of LAF
Let us take a numerical example to illustrate the functioning of the Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF). Suppose the RBI wants to inject liquidity into the banking system. It conducts a Repo transaction with a bank, buying government securities worth Rs. 1 crore. The bank sells the securities to the RBI and receives Rs. 1 crore in cash. The transaction is reversed after a specified period, say 7 days. During this period, the bank pays interest on the borrowed amount at the Repo Rate, say 5%.
After 7 days, the bank buys back the government securities from the RBI, paying Rs. 1 crore plus interest of Rs. 2,397 (calculated as 1,00,00,000 * 5%/365 * 7). The RBI has injected liquidity into the system by lending money to the bank, which can now use the cash to lend to other banks or businesses.
The importance of LAF in maintaining financial stability
The Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) is an important tool for maintaining financial stability. It allows the RBI to manage liquidity in the banking system and signal its monetary policy stance. By injecting or absorbing liquidity from the system, the RBI can influence interest rates and inflation, which are key drivers of financial stability.
Without the LAF, the banking system would be prone to liquidity mismatches and credit crunches, which can lead to a financial crisis. The LAF ensures that banks have access to funds when they need them and that the system functions smoothly.
The impact of LAF on interest rates and inflation
The Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) has a significant impact on interest rates and inflation. When the RBI conducts Repo transactions, it injects liquidity into the system, which increases the supply of credit and reduces interest rates. On the other hand, when the RBI conducts Reverse Repo transactions, it absorbs liquidity from the system, which reduces the supply of credit and increases interest rates.
The impact of the LAF on inflation is indirect but significant. By influencing interest rates, the LAF affects the cost of borrowing and lending, which in turn affects the demand for goods and services. When interest rates are low, consumers and businesses tend to borrow more, leading to higher demand and inflation.
Criticisms and challenges faced by the RBI in implementing LAF
The Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) has been criticized for being too complex and difficult to understand. Some experts argue that the RBI should simplify the LAF and communicate its functioning more effectively to the public.
Another challenge faced by the RBI in implementing the LAF is the risk of moral hazard. When banks know that they can borrow from the RBI at any time, they may take on excessive risk, knowing that the RBI will bail them out in case of a crisis. To mitigate this risk, the RBI has introduced various prudential norms and guidelines for banks.
Conclusion: The significance of LAF in the overall financial system of India
In conclusion, the Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) is a crucial tool for maintaining financial stability in India. It allows the RBI to manage liquidity in the banking system and signal its monetary policy stance. By injecting or absorbing liquidity from the system, the RBI can influence interest rates and inflation, which are key drivers of financial stability.
However, the LAF is not without its challenges. The RBI must communicate its functioning more effectively to the public and mitigate the risk of moral hazard. Despite these challenges, the LAF remains an important component of the overall financial system of India, ensuring that the system functions smoothly and efficiently.
CTA: As we have seen, the Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) is a crucial tool for maintaining financial stability in India. As investors and analysts, it is important to understand the functioning of the LAF and its impact on the financial system. I urge you to read more about the LAF and other monetary policy tools used by the RBI to gain a deeper understanding of the Indian financial system.










