Table of Contents
In the realm of monetary control, open market operations (OMOs) play a crucial role in managing liquidity in the financial system. OMOs are actively utilized to regulate excess liquidity, stabilize domestic money markets, and influence the availability and cost of credit. Developed countries like the UK and USA have long recognized the significance of OMOs in maintaining financial stability. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of OMOs in India, their objectives, implementation, and impact on various stakeholders.
Understanding Open Market Operations
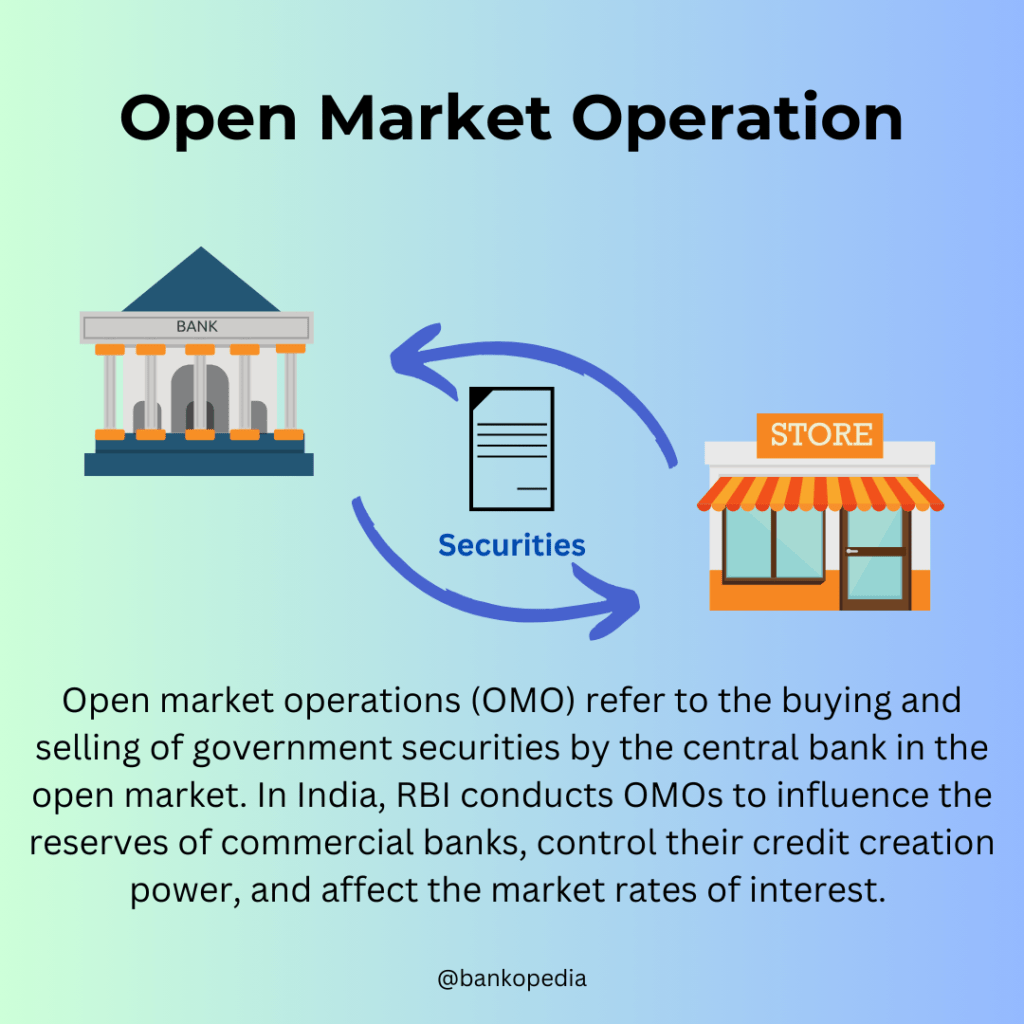
Open market operations refer to the buying and selling of government securities by the central bank in the open market. In India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) conducts OMOs to influence the reserves of commercial banks, control their credit creation power, and affect the market rates of interest. These operations directly impact the availability and cost of credit, thereby influencing the broader economy.
Objectives of OMOs
The primary objectives of OMOs in India are twofold:
- Reserves Influence: OMOs are utilized to influence the reserves of commercial banks. By buying or selling government securities, the RBI alters the surplus cash resources available with banks, thereby impacting their capacity to create credit.
- Interest Rate Control: OMOs are employed by the RBI to affect the market rates of interest. Through open market purchases or sales of government securities, the central bank influences the overall money supply and, consequently, the cost of credit.
Implementation of OMOs
OMOs in India involve the sale or purchase of government securities by the RBI. When the central bank sells government securities, it withdraws a portion of the deposit resources of banks, thereby reducing their lending capacity. On the other hand, open market purchases of securities lead to an expansion in the supply of bank credit and an increase in money supply.
It is important to note that OMOs do not alter the total stock of government securities but rather change the proportion held by the RBI and commercial and cooperative banks. Open market sales result in a reduction in the net eligible credit to the government by other banks, while open market purchases lead to an expansion in the credit extended to the government.
Impact of OMOs
The implementation of OMOs has a significant impact on various stakeholders and the overall economy. Let’s explore the effects of OMOs on different aspects of the financial system:
1. Liquidity Management
OMOs are an essential tool for liquidity management. When there is excess liquidity in the system, the RBI conducts open market sales to absorb the surplus funds. Conversely, during periods of liquidity crunch, the central bank resorts to open market purchases to inject liquidity into the system. OMOs help maintain stable liquidity conditions in the financial markets.
2. Interest Rates
One of the primary objectives of OMOs is to influence market interest rates. When the RBI sells government securities, it reduces the surplus cash resources of banks, leading to a contraction in the supply of bank credit. This, in turn, affects the overall interest rates in the economy. Conversely, open market purchases of securities increase the surplus cash resources of banks, leading to an expansion in credit and potentially lower interest rates.
3. Credit Creation
OMOs directly impact the credit creation capacity of commercial banks. When the RBI sells government securities, it reduces the surplus cash resources of banks, limiting their ability to create fresh loans. Conversely, open market purchases of securities increase the surplus cash resources, augmenting the credit creation capacity of banks. The availability and cost of credit are closely linked to the implementation of OMOs.
4. Government Securities Market
OMOs also play a crucial role in the government securities market. By conducting open market sales and purchases, the RBI alters the composition, maturity structure, and yield of government securities. The central bank can buy, sell, or hold government securities of various maturities without any restrictions. OMOs help in maintaining a vibrant and active market for government securities.
5. Monetary Policy Transmission
OMOs are an integral part of the monetary policy transmission mechanism. By influencing interest rates, credit availability, and liquidity conditions, OMOs impact the effectiveness of monetary policy in achieving desired macroeconomic objectives. The RBI utilizes OMOs to align the monetary policy stance with its broader objectives of inflation control, economic growth, and financial stability.
Recent Developments and Future Outlook
Over the years, the OMO market in India has evolved significantly. Various measures have been taken to promote both primary and secondary markets in government securities, making OMOs more active and effective. The RBI has introduced private placements and selective sales of securities based on market conditions. The central bank has also expanded its purchase list to include a wider range of securities, ensuring flexibility in conducting OMOs.
The recent focus has been on augmenting the stock of marketable securities for active OMOs. Special securities have been converted into marketable securities of different maturities to enhance liquidity management. Additionally, the RBI has utilized OMOs to absorb excess liquidity resulting from capital inflows and maintain stable domestic interest rates and exchange rates.
Looking ahead, OMOs will continue to play a vital role in liquidity management and monetary control in India. With ongoing reforms and developments in the government securities market, OMOs will remain a key tool for the RBI to regulate credit creation, manage interest rates, and ensure financial stability.
Open market operations are an essential tool in the arsenal of central banks for managing liquidity and influencing key financial variables. In India, the RBI utilizes OMOs to regulate the reserves of commercial banks, impact interest rates, and maintain stability in the financial system. OMOs have a significant impact on liquidity management, credit creation, and the government securities market. As the Indian economy continues to evolve, OMOs will play a crucial role in shaping monetary policy and ensuring financial stability in the years to come.











2 thoughts on “Open Market Operations: A Key Tool for Liquidity Management in India”